Types of Hormones in the Human Body

Hormones are the body’s chemical messengers that deliver signals that control almost all of the major functions that keep us alive and healthy. Among the various types of hormones in the human body, we find chemicals that influence metabolism, libido, digestion, brain functions, glucose uptake, stress, fertility, and more.
When we look at how many types of hormones in the human body keep us going, we can either count them by the sheer number or the types.
There are 4 main types of hormones:
- Amino acids
- Eicosanoids
- Peptides
- Steroids
According to different lists, there may be anywhere from 50 to over 60 different types of hormones in the human body; however, you will find over 70 in our list below.
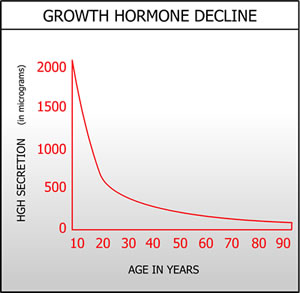
Some of these hormones have the sole purpose of stimulating the release of other such chemicals. Others, such as growth hormone, have vast effects throughout the body.
In the charts below, we will show the type, name, producer, and functions or effects of each hormone.
Here are the different types of hormones in the human body and their functions:
Amino Acids
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Epinephrine also known as Adrenaline | Adrenal gland | Blood pressure, increases heart rate, glycogenolysis (liver), lipolysis, fight or flight response, muscle contraction, respiratory rate vasoconstriction and vasodilation |
| Melatonin | Pineal gland | Circadian rhythm, sleep |
| Triiodothyronine | Thyroid gland peripheral tissue | Increases metabolism, cardiac output, heart and ventilation rates |
| Thyroxine | Thyroid | Metabolism regulation |
Eicosanoids
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Prostaglandins | Made by chemical reactions as needed | Help the body deal with injury and tissue damage, blood clot formation, inflammation, labor induction |
| Leukotrienes | White blood cells | Increase vascular permeability, helps with asthma attacks and allergies |
| Prostacyclin | Endothelium | Inhibits platelet activation, vasodilator |
| Thromboxane | Platelets | Vasoconstriction |
Peptides
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Amylin | Pancreas | Inhibits digestive secretion and reduces food intake |
| Anti-Mullerian hormone | Testes | Inhibits prolactin and TRH release |
| Adiponectin | Adipose tissue | Modulates glucose and lipid metabolism |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (corticotropin) | Anterior pituitary gland | Synthesis of corticosteroids |
| Angiotensinogen and angiotensin | Liver | Vasoconstriction, releases aldosterone |
| Antidiuretic hormone | Posterior pituitary | Water retention in kidneys, ACTH release, moderate vasoconstriction |
| Atrial-natriuretic peptide (atriopeptin) | Heart | Vasodilator |
| Brain natriuretic peptide | Heart | Dilates |
| Calcitonin | Thyroid | Helps regulate calcium and inhibits osteoclast breakdown of bone |
| Cholecystokinin | Duodenum | Aids digestion and reduces appetite |
| Corticotropin-releasing hormone | Hypothalamus | Influences cortisol release |
| Cortistatin | Cerebral cortex | Induces slow-wave sleep |
| Enkephalin | Kidney | Pain regulator |
| Endothelin | Vascular endothelium | Smooth muscle contraction |
| Erythropoietin | Kidney | Stimulates production of erythrocytes |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone | Anterior pituitary | Spermatogenesis in males, maturation of Graafian follicles in female ovaries |
| Galanin | Gastrointestinal tract and CNS | Water balance, osmotic regulation energy homeostasis |
| Gastric inhibitory polypeptide | Duodenum and jejunum mucosa | Induces insulin secretion |
| Gastrin | Stomach, duodenum | Gastric acid secretion |
| Ghrelin | Stomach | Appetite stimulator |
| Glucagon | Pancreas | Increases blood glucose levels, liver glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 | Ileum | Synthesis and release of insulin |
| Gonadotropin-releasing hormone | Hypothalamus | Stimulates FSH and LH secretion from pituitary |
| Growth hormone-releasing hormone | Hypothalamus | Stimulates GH release from pituitary |
| Hepcidin | Liver | Inhibits cellular iron export |
| Human chorionic gonadotropin | Placenta | Supports corpus luteum at pregnancy onset |
| Human placental lactogen | Placenta | Increases insulin and IGF-1 production, insulin resistance, carbohydrate intolerance |
| Growth hormone (somatotropin) | Anterior pituitary | Stimulates cellular reproduction, IGF-1 secretion, metabolism, immunity, libido, and more |
| Inhibin | Ovaries, testes, fetus | Inhibits FSH production |
| Insulin | Pancreas | Controls glucose levels |
| Insulin growth factor (somatomedin) | Liver | Supports cellular reproduction, mediator of many growth hormone effects |
| Leptin | Adipose tissue | Decreases appetite and supports metabolism |
| Lipotropin | Anterior pituitary | Stimulates melanin production, lipolysis, steroidogenesis |
| Luteinizing hormone | Anterior pituitary | Female ovulation and male testosterone production |
| Melanocyte stimulating hormone | Anterior pituitary, pars intermedia | Melanogenesis in hair and skin |
| Motilin | Small intestine | Gastric activity |
| Orexin | Hypothalamus | Wakefulness, increases appetite and energy expenditure |
| Osteocalcin | Bones | Testosterone synthesis, muscle function, memory formation, energy expenditure |
| Oxytocin | Posterior pituitary | Stimulates breast milk, circadian homeostasis, cervical and vaginal contraction |
| Pancreatic polypeptide | Pancreas | Regulates pancreatic and gastrointestinal secretions, affects hepatic glycogen levels |
| Parathyroid hormone | Parathyroid | Activates vitamin D, increases blood calcium and reabsorption in kidney |
| Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide | Multiple | Induces hypophysis activity, is a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator |
| Prolactin | Anterior pituitary | Milk production, sexual gratification |
| Prolactin releasing hormone | Hypothalamus | Prolactin secretion |
| Relaxin | Uterus, placenta, mammary glands, corpus luteum | Relaxes pelvis ligaments, softens and widens cervix for childbirth |
| Renin | Kidney | Regulates blood pressure |
| Secretin | Duodenum | Stimulates liver and pancreas secretions |
| Somatostatin | Hypothalamus, gastrointestinal system, pancreas | Inhibits growth hormone, insulin, thyroid stimulating hormone, cholecystokinin |
| Thrombopoietin | Kidney, liver, striated muscle | Produces platelets |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) | Anterior pituitary | Stimulates thyroxine and triiodothyronine secretion |
| Thyrotropin-releasing hormone | Hypothalamus | Regulates thyroid gland activity and thyroid stimulating hormone secretion |
| Vasoactive intestinal peptide | Pancreas, | Heart contractility, vasodilation, glycogenolysis, lowers blood pressure, reduces inflammation |
| Guanylin | Epithelium | Regulates intestinal water and salt transport |
| Uroguanylin | Renal tissues | Regulates renal water and salt transport |
HT Medical Center provides blood analysis to detect the most common forms of hormone deficiency or imbalance in adults over thirty.
Steroid Hormones – In a Class All Their Own
The steroid hormones come from three places:
- The testes
- The ovaries
- The adrenal glands
The basis of all steroid hormones is cholesterol. Steroid hormones are identified as either adrenal or sex hormones as shown in the classifications below:
Glucocorticoid
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Cortisol | Adrenal cortex | Anti-inflammatory, controls blood sugar levels, salt and water balance, influences memory formation, stress hormone |
Mineralocorticoid
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Aldosterone | Adrenal cortex | Increases blood volume by absorbing sodium in kidneys |
Androgens
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Testosterone | Testes, ovaries, adrenal glands | Libido support, muscle and bone growth, brain functions, hair growth |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone DHEA | Ovaries, testes, kidneys | Precursor hormone for testosterone and estrogen |
| Androstenedione | Adrenal glands, gonads | Stepping stone for estrogen and testosterone production |
| Dihydrotestosterone | Multiple, enzyme 5 alpha reductase converts testosterone into DHT | Stimulates development of male characteristics, too much can lead to prostate growth and hair loss |
Estrogens
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Estradiol | Ovaries, testes, aromatase converts testosterone into estradiol | Uterine and endometrial growth reduces bone resorption, maintains blood vessels, assists with platelets and circulation, increases growth hormone, cortisol, and SHBG, promotes lung functions, and more |
| Estrone | Ovaries | Least abundant form of estrogen |
| Estriol | Placenta | Role in pregnancy is unknown, may help with hot flashes and menopause symptoms |
Progestogen
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Progesterone | Ovaries, testes, adrenal glands, placenta | Assists thyroid hormone functions, pregnancy support, source hormone, regulates estrogen effects, nerve functions, anti-inflammatory, normalizes blood clotting, and more |
Secosteroids
| NAME | PRODUCER | FUNCTION/EFFECT |
| Calcitriol (1,25 – dihydroxy vitamin D 3) | Skin/proximal tubule of kidneys | Active form of vitamin D 3 Increases calcium and phosphate absorption |
| Calcidiol (25 – hydroxy vitamin D 3) | Skin/proximal tubule of kidneys | Inactive form of vitamin D 3 |
Most Common Hormone Deficiencies in Adults
While any hormone deficiency can cause a particular problem, some create widespread havoc that can lead to serious health concerns such as heart disease, diabetes, osteoporosis, dementia, obesity, atherosclerosis, and other medical issues.
What types of hormones in the human body create the biggest problems if they become deficient?
Somatotropin (growth hormone) deficiency can impact metabolism, libido, immunity, cellular regeneration, and even brain functions.
Low testosterone can impact red blood cell production, metabolism, brain functions, libido, muscle development, and bone density.
Considering there are so many different kinds of hormones in the human body that can affect daily functions and well-being, it is crucial to ensure that their levels are maintained at a healthy state.
Find out more about hormone deficiency and treatment by contacting HT Medical Center.